Andean Corridor to Cross International Border and Provide Connectivity for Wide-Ranging Species
08/16/2022
Nature and Culture is working to develop a connectivity corridor that spans 5 million acres, protecting key ecosystems and diverse habitats.
We are working with community partners and government officials to develop the first “bi-national” corridor in South America. The proposed Andean Corridor will connect mountain habitats in southern Ecuador and northern Peru, creating an intact biological corridor that crosses international borders. The end result will unite three of our existing landscape mosaics. With this corridor, wide-ranging species that traverse the area will have unencumbered mobility in their natural habitat.
Nature and Culture Spotlights Connectivity
The Andean Corridor was initially set in motion fifteen years ago with the establishment of our Sangay Podocarpus mosaic, Ecuador’s first connectivity corridor. The impetus for this mosaic was a noteworthy gap in protected areas between Sangay National Park and Podocarpus National Park in the southern Ecuadorian Andes. Because our conservation model values connectivity, we partner with local expert conservationists to customize conservation areas based on the needs of endangered species.
Since the establishment of the Sangay Podocarpus mosaic, we’ve added 11 protected areas in the region. The Andean Corridor will expand this area even further to 236 miles along the Andes thus linking a chain of protected areas.
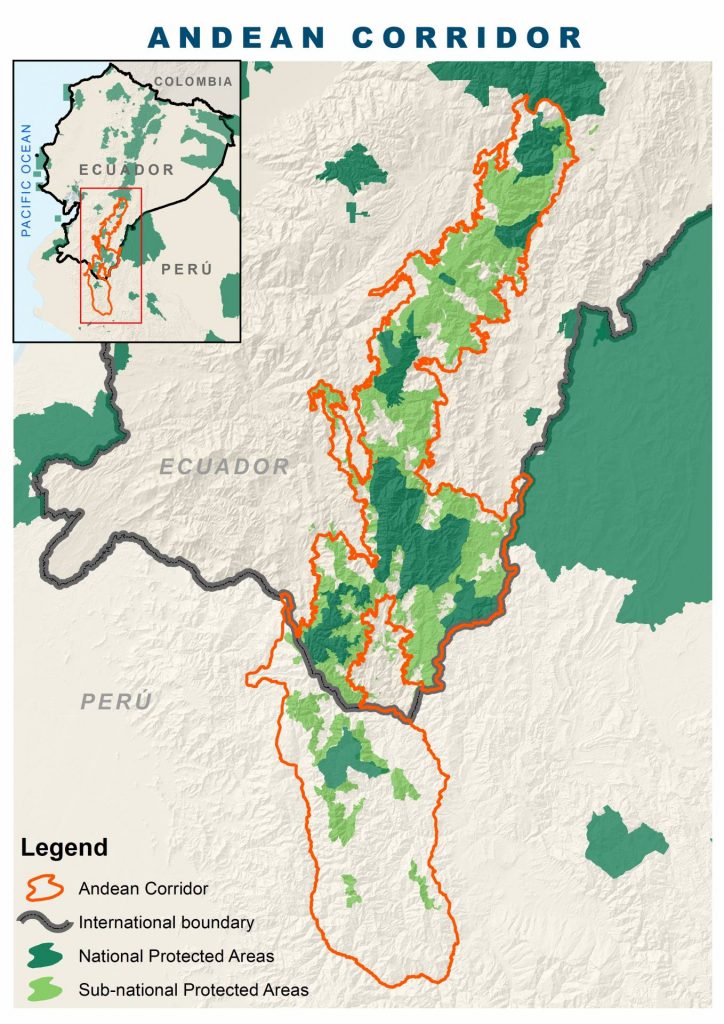
Three of our Landscape Mosaics Already Contribute to the Andean Corridor
The Sangay Podocarpus and Podocarpus El Cóndor mosaics in Ecuador span the páramo grasslands, montane forests, and cloud forest ecosystems. Whereas the North Andes mosaic in Peru encompasses some of the most diverse, fragile, and complex cloud forests on Earth.
Overall this region encompasses some of the most biologically diverse places on our planet. The Tropical Andes are a global biodiversity hotspot. For example, the area contains about one-sixth of all plant life in the world and boasts the largest variety of amphibian, bird, and mammal species. Its ecosystems help to regulate the natural cycles that produce and renew the planet’s air, water, and climate.
Species Monitoring to Improve Conservation Efforts
Habitat range is a strong indicator of species’ vulnerability. By combining ecosystems together into landscape mosaics, networks of wildlife movement are protected. This helps maintain whole species’ survival.
Some wildlife travel long distances to migrate seasonally, others need to disperse away from their natal groups to find new home ranges to prevent inbreeding and competition. For these wide-ranging species, like the Andean bear that can traverse up to 150 miles of terrain a day, protecting these far-reaching ecosystems means giving these animals adequate room to roam.
To learn more about how we are partnering with local wildlife specialists, watch our panel discussion, Conserving Habitat for Wide-Ranging Species in the Andes. Our team and local species specialists presented on the conservation needs of three wide-ranging, endemic species — the Andean bear, black-and-chestnut eagle, and the pampas cat.


